The global shift toward electric mobility is one of the primary drivers of SiC adoption. EVs require highly efficient power electronics for key systems like:
- Traction inverters (convert DC from the battery to AC for the motor)
- Onboard chargers (OBCs)
- DC-DC converters
SiC devices offer faster switching, reduced heat generation, and higher efficiency, which translates to longer driving range, shorter charging times, and smaller battery packs. Leading EV manufacturers are already adopting SiC in their latest models to gain a competitive edge.
Real-World Example: Tesla’s Use of SiC
Tesla’s Model 3 was one of the first mass-market EVs to feature a SiC-based inverter, resulting in a significant improvement in energy efficiency. Other automotive giants are following suit, with plans to integrate SiC technology across their entire EV product lines.
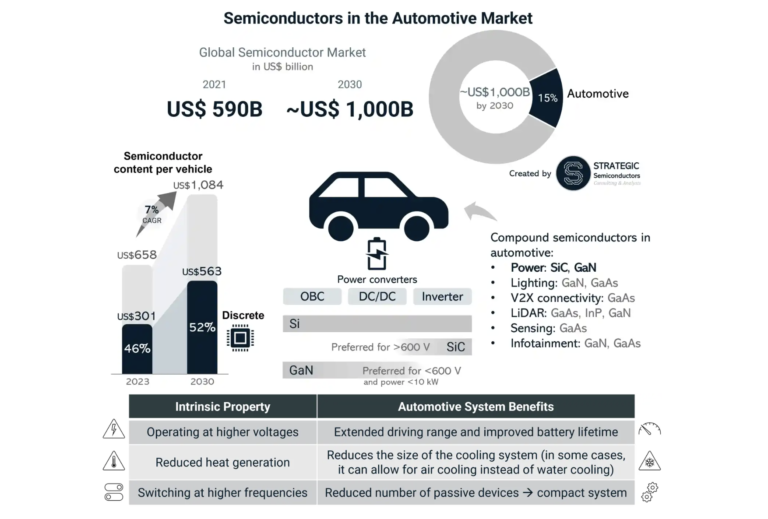
Reference: https://www.eetimes.eu/sic-and-gan-drive-vehicle-electrification/
Benefits of SiC in EVs
- Longer range: SiC’s efficiency allows EVs to travel farther on a single charge
- Faster charging: SiC’s efficiency allows EVs to charge faster
- Lower costs: SiC’s efficiency can help reduce the overall cost of an EV
- More reliable operation: SiC’s reliability can improve the performance of an EV
- Better thermal management: SiC’s thermal conductivity helps manage heat in an EV
How SiC is used in EVs
- SiC MOSFETs are transistors used in the power electronics of EVs
- SiC FETs are used in EVs to improve the efficiency of high voltage power systems
- SiC inverters are used in EVs to convert DC power from the battery to AC power for the electric motors